Posts Categorised: SEO
How fast your website loads is important if you want other people to see it.
Why? Every second your customers are delayed waiting for your site to load – you’re losing money.
According to Neil Patel, “If an e-commerce site is making $100,000 per day, a 1 second page delay could potentially cost you $2.5 million in lost sales every year”.
“2 seconds is the threshold for ecommerce website acceptability. At Google, we aim for under a half second.”
Maile Ohye, Google
One – two – three.
If your site hasn’t loaded in that amount of time, your visitor is gone. Probably never to come back.
Another problem with a slow loading site is search engine ranking.
Google checks about 200 different factors to determine where your site will rank for a particular key word or phrase. If you’re the only veterinarian in Anytown, USA then Google doesn’t have much choice. If someone searches for “veterinarian in Anytown, USA” your site will show up (probably).
But if your business is one of many similar businesses in the area, you need to do more to rank well in the search results. Page speed is one of the most important factors.
“Although speed has been used in ranking for some time, that signal was focused on desktop searches. Today we’re announcing that … page speed will be a ranking factor for mobile searches.”
Your options –
Okay, you just checked your own website and it seems to load pretty fast, so what’s the big deal? Well you’ve probably checked your website before and some of it is cached on your computer or phone. That means it didn’t have to download those pieces before it could start displaying the website. Someone new to your website doesn’t have that cache, so you’d better hope they have patience.
Your other option is taking the time to optimize your website. There is an updated tool that can help you determine what to do.
Here are some things you can check with Google’s tool:
- The speed of both the entire site and of individual pages
- Whether the site/page speed is faster or slower compared to the prior month
- Whether the site speed/page speed ranks Fast, Average, or Slow
- How the site speed compares to others in the industry
- The potential impact of site speed on revenue
- A detailed list of recommended fixes to increase speed on up to 5 pages on the site
Go check your website now at: https://www.thinkwithgoogle.com/feature/testmysite
Give us a call for help in speeding up your site if you get a poor grade – and especially if you get an “F” (gasp!).
Is your website working as hard for you as it can? Does it show up in the search results for your service or product?
If you answered ‘No’ to either question, you probably need to optimize your website – Search Engine Optimization or SEO for short.
You can read about SEO and see if you’d like to tackle it yourself. Or you might think it would be smarter to hire a pro to help.
But how do you choose the best search engine marketing firm?
There are lots of choices. Some are good. Some can get great results, but use risky tactics. Some were good, but haven’t kept up with the latest SEM tactics. Plus there are many scam artists.
To help you out, here is a list of some warning signs.
- Be careful of a firm that mass mails. A good SEM/SEO firm is generally too busy to be sending junk mail.
- Be careful of someone who guarantees a number one ranking or even a page one ranking. Particularly if they say they can do it quickly. Although they may be able to it, most likely it will be for junk keywords. What good will it do you to rank high if no one is searching on those keywords?
- Be careful of a firm that won’t tell you how they will get you better rankings. Their ‘secret magic’ may wind up getting your website banned.
- Be careful of fake testimonials. If someone is doing work online their testimonials should include a link to the actual client’s website. I’ve seen some so shady they’ve actually included fake video testimonials that were probably made by Fiverr sellers. One ‘seo expert’ had a testimonial video from an optometrist – a profession that requires licensing – and, nope, the ‘optometrist’ is either unlicensed or just plain doesn’t exist.
- Be careful of fake or spammy backlinks. Backlinks are important for ranking well in the search engines. Recently Google cracked down on poor quality backlinks, but a technique that still works (sometimes) is creating a lot of websites and including a link from each of these sites back to the client’s website. If the content on each of these websites is original and useful, I would call that a gray-hat technique. Unfortunately that’s not always the case. I found another ‘SEO guru’ who had several backlinks from websites that looked, at first glance, to be legitimate. The sites seemed well designed with appropriate page titles and subtitles, but upon looking closer every bit of content was the sample Latin gibberish many programmers use.
- Be careful of someone who uses black-hat techniques and even some gray-hat techniques. If you decide to work with them, be sure you know the risks. Your website could move up the rankings quickly, which can be a good thing. But if it moves up too quickly or if Google suspects something shady you could lose your ranking or even disappear completely from the search results. It could even happen despite what looks like white-hat techniques used on your site, if Google can connect your site to someone who is using black-hat techniques.
Good luck with your search and remember, if it seems to good to be true, it probably isn’t.
Contact us if you’d like some help with your rankings. We’d be glad to tell you about our services and see if we’d be a good fit.
Anchor text is part of a link and links are the lifeblood of the Internet. They allow users to click to another source of information they might find interesting.
The part of the link that we can see is called the anchor text. This portion often gives the visitor some descriptive information about where that particular link will go.

Sometimes the links will go to a page on another website or it might go to another page within the current website. The link might even go to a section of another page.
Anchor text is important to search engines
Search engines use links to travel around the web and gather information. This text also helps the search engines determine the topic of the pages they’re linking to.
For example if most of the links pointing to a particular page says something like “dog grooming in Denver” (or something very similar) the search engines are pretty confident that that page is going to be about dog grooming in Denver.
The anchor text also works something like a vote. In the example above, the website with the link is saying the content on the website “example.com” is relevant for “blue widgets.” The Example website would rank well in the search results for “blue widgets” if several other websites also used that term in their links.
Trap of over optimizing links
In 2012 Google released the “Penguin” update which changed the way it handled anchor text. This update discouraged over optimization.
For example it would look unnatural for a site to have a majority of inbound links using the same term of “blue widgets”. In other words it looked like the company had been specifically building links rather than allowing them to happen naturally.
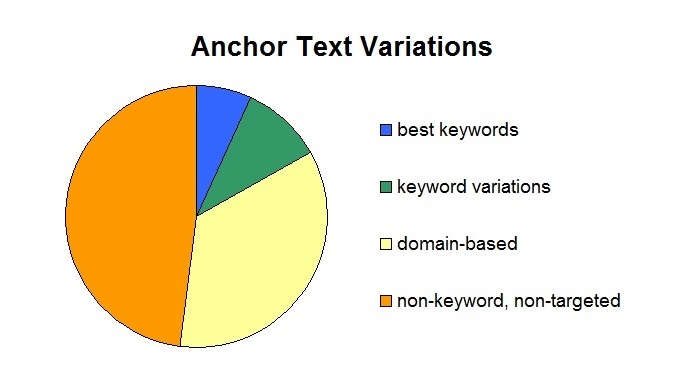
People generally use a variety of terms to describe the contents of an article. Some might use the article’s title or URL address, while others might use something generic like “click here.” Or they might describe what they learned, such as “blue widgets can increase speed.”
Tips
When you’re trying to decide what text to use try thinking of what the visitor might learn on that page. For example, “how to gather honey” or “avoid being stung” rather than just “bees.” This also helps the search engines distinguish between your various articles on similar topics.
For SEO purposes though, you’ll want a variety of anchor text in your inbound links. Based on the types of links listed above, you should have no more than 15-20% of your inbound links using your keywords and variations of your keywords. Then another 30-40% using some form of your URL:
- http://www.example.com
- http://www.example.com/
- http://example.com
- http://example.com/
- www.example.com
- example.com.
The majority of your inbound links should be something generic, for example “click here” or “this” or “more details” even though it doesn’t give the visitor any helpful information.
If you’re not sure about the variations in your inbound links, go to MajesticSEO and enter your website’s URL in the search box. You’ll see a lot of information, but for now scroll down to see the Anchor Text graph. Also try checking some of the authority sites in your niche to see the diversity in their links.
If you notice your anchor text is too keyword-rich, there are a couple of quick ways to fix it. Do a search for “article directories” and read their submission guidelines. Then write an article for each, using some non-keyword anchor text. Then search for “press release submission” and repeat. No, Google doesn’t give much weight to these types of backlinks, but they can help make your anchor text diversity look more natural.
One last tip, make sure you’re linking to the page you want – http://www.example.com/page.htm – rather than the just the domain – http://www.example.com.
What is it?
Search Engine Optimization is using both on-site and off-site techniques to increase a website’s ranking in the search results for the resulting increase in traffic.

There are lots of strategies – varying from white-hat to black-hat – to help a website rank better. Most of the strategies will fit within five basic categories:
Keyword research – Researching keywords for each page, paying attention to search volume, the amount and quality of competition and the likelihood of ranking for those words and phrases. However overusing keywords can lead to a penalty. The trick is using them enough so visitors and search engines know what the page is about, without using them so much the text sounds unnatural.
On-page optimization – Writing content specific to those keywords, including using those words and phrases in particular places on the page, but not overdoing their usage.
Site technology – Ensuring the website and page structures are optimized for both visitors and search engines. These include how fast the page loads, whether there are header tags and a page description and whether the page can even be found within the website.
Social media marketing – Sharing content and growing the website’s visibility in social media to increase brand awareness and increase social signals. Greater visibility of good content increases the chance more people will find it and link to it.
Building backlinks – Encouraging people to link back to content on another website. Building backlinks has been the focus of SEO for many years, but the popularity led to unnatural link building which often leads to penalties.
Here are some resources if you’d like to learn more …
What is Anchor Text and Why is it Important?
13 Tips to Optimize Your Pages for Google
Search engine optimization is constantly evolving. What worked and was accepted just a few years ago may be frowned on today.
Whether a particular tactic is acceptable, depends on why and how it’s done.
For example, in the beginning guest blogging was considered a badge of honor because someone “thought your content was awesome enough or that you were important enough that they would republish something you wrote on their site.”
Unfortunately, for some people guest blogging evolved into a quick way to ‘earn’ a backlink instead of a way to share quality content. Spammy content, disguised as a guest post, was everywhere. But perhaps because there were bloggers producing quality posts for other blogs, Google looked the other way. For awhile.
Then in January 2014, Matt Cutts said “stick a fork in it: guest blogging is done.”
The online community set up such a hue and cry that Matt went on to clarify what he meant. Guest blogging in exchange for backlinks was frowned on, but guest blogging for good reasons such as exposure, branding and increased reach was still okay. The main focus seems to be why. Some of the things Google might look at to determine the intent of the post include:
- the quality of the post,
- whether it includes dofollow backlinks,
- plus perhaps the author having a history of doing many guest posts.
So some practices can be good or bad, depending on why and how. There are, however, some practices that are just bad. Some practices may be caused by inexperience. Other practices, like hiding text or buying links, can be someone’s attempt to get better rankings with the thought it shouldn’t be wrong because they aren’t hurting anyone else.
Then there are practices that are immoral and sometimes just plain illegal. Check out the infographic below for more information. If you find it helpful, feel free to share it. Oh, and, may the force be with you!
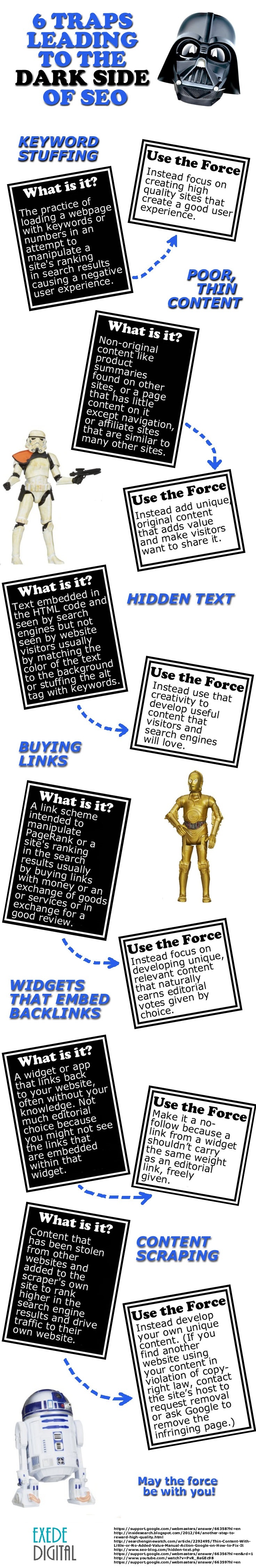
Share this Image On Your Site
An important part of nudging your website higher in the search results is earning backlinks.
What Are Backlinks?
Backlinks are links on other websites pointing to your website or page. They’re also called incoming or inbound links.
They help visitors and search engines discover your content via anchor links on other websites and web services.
Why Are Backlinks Important?
It’s because someone thought your content was good enough to share with their own visitors by linking to it. Each backlink acts like a vote.
Search engines use backlinks as a vote in deciding your website’s search engine ranking. The more votes, the better. But more important is the quality of the link – which includes the ranking of the site linking to your page, the anchor text used and the relevancy of both websites.
So, for example, a link from a high-ranking website like The NY Times would count for more than a link from Joe Schmoe’s blog because of overall quality. However if Joe’s blog has quality content AND is in your same industry, it could count for more than a link from a well known website because it’s probably more relevant.
Another example might help. A link from a French restaurant pointing to the country veterinarian’s website probably wouldn’t help much because they’re in different industries. However… if there was a bacterial outbreak and this veterinarian is the USDA inspector for the meat served in the restaurant and he says this particular meat passed inspection, the link would make more sense. It would be relevant.
Search engines also analyze the anchor text because it’s usually relevant to the linked-to page. (There’s that word again.) Most important is whether the anchor text helps a visitor understand what type of content they’ll find when they click on the link.
History
To better understand what can help – and what can get you in trouble – we need to take a look at what’s happened in the past.
Back in the stone age of the Internet, Yahoo and AltaVista were the best-known search engines. They looked mainly at information webmasters put in meta tags and at keyword density to figure out what a page was about and used that to decide on rankings.

Unfortunately that led to keyword stuffing – the more the merrier – both on the page and in the meta tags. If the website owner thought there was a chance – even a teeny one – that the site would rank for a certain word or phrase, they added it. It didn’t matter much if it had anything to do with the actual content on that page. That made it hard for the search engines to tell what a particular page was really about.
Then Google came on the scene and started looking at the number of inbound links to a website. They reasoned if someone was willing to link to a website, it must be good. So the more backlinks, the higher the ranking.
At first it worked well because the search results were more relevant. Then people figured out how to ‘game’ the system and link farms were born. Everyone wanted links and it didn’t matter how they got them. The sheer number of backlinks was the only thing of importance.
Lots of crummy websites ranked high. For awhile.
Google took note and updated their algorithms. You may have heard of the Panda and Penguin updates.
After Panda, websites with rankings based on poor quality backlinks tumbled. Hard. Roughly 12% of searches were affected.
Penguin targeted websites that over-optimized the anchor text in the backlink. Basically, webmasters had found a way to stuff keywords into their backlinks. They were putting their main keyword into every backlink, hoping that would help the website rank high for that keyword. But in natural linking, the main keyword isn’t used very often. In most cases, the anchor text would be something generic, like ‘click here’ or ‘Acme Co’ or the website address.
These updates were aimed at webmasters who tried to game the system. Instead of providing quality content, they took shortcuts to get their websites ranked higher. As Google learns more about these black-hat techniques, the search engine results get better and more relevant.
What Does The Future Hold?
Here is a video of Matt Cutts, head of search at Google, discussing backlinks and the future. He believes backlinks will still be important for many years, however Google continues to work on more ways to determine whether a page meets a user’s expectations.
In a nutshell, backlinks are still important, as are the quality of the content and the reputation of the site.
How Do You Build Backlinks?
Now that you know why you should get backlinks and how the search engines have evolved, you need to know how to develop backlinks today.
Start by spying on your competitors to see where their backlinks are coming from and maybe add those links to your website.
- Search for your keywords and phrases in Google.
- Copy the URL for the top result – just make sure you’ve chosen a search result and not an ad.
- Go to Alexa.com and where it says ‘Enter a site’, paste the URL and click Go. Scroll down to the section ‘Total Sites Linking In’ and make a note of each site listed as a backlink.
- Go back to the search results and copy the URL for the next listing, submit on Alexa and make a note of each backlink. Repeat for the top 5-10 Google results for your keywords.
- Take a look at each of the backlinks you’ve collected. Some may be good, some may be questionable and some may be terrible. Try to get backlinks from the good sites, but only if they’re relevant to your website.
- When you find backlinks from directories, submit your website’s link there too.
- When you find backlinks from forums, sign up and include your link in your profile or comments.
- When you find backlinks from social sites, add some content of your own and include your link.
- When you find backlinks from websites and blogs, check to see if you can guest post in exchange for a link.
More ideas that we’ll be covering in detail in future posts include:
- Sharing your content on social media website such as Facebook, Twitter, Google , Pinterest and others. Social signals and links can help increase your rankings.
- Posting your content on Reddit.com and Delicious.com. Just remember not to post only your own content and look like a spammer. You don’t want to be banned.
- Posting your own videos on YouTube.com and including links back to your website.
- Submitting press releases online when your company does something news worthy. You can try some of the free sites, but to get the most link juice use the paid versions like PRWeb.com to syndicate your press release to a large number of news and TV station websites, local newspaper websites, popular blogs, and other mainstream web properties.
- Write original content and submit to article directories. But be careful because some article directories were created as link farms and have been de-listed from the search results. A link from a directory like that would hurt your search rankings. Also submitting the same article to many directories will hurt your rankings and possibly cause your website to be de-listed.
These are only a few suggestions to consider. Just remember to try for quality and relevant links for the best results. It can be a long, slow process. Don’t be seduced by the dark side into trying to build links too fast or accepting spammy backlinks. You want your website to grow and prosper, not go spinning off into a black hole.
What have you tried? And how well did it work?
You might also like:
- Learning more about how search works
Today is not only Friday the 13th, but it’s also the day of the full moon. So in honor of both, here are 13 ways to make your pages shine brightly.
1. Provide quality content.
Google describes a site with quality content as “helpful, information-rich … pages that clearly and accurately describe your topic.” Also “think about the words users would type to find your pages and include those words on your site.”
- Concentrate on one topic per page. If it’s a larger topic, concentrate on one portion of the topic per page. For example, instead of trying to explain gardening on one page, break it up. You might have one page on preparing your garden site, another page on choosing the right tools, another page on growing a garden in the shade, and even those topics can be broken down some more.
- Use your unique knowledge and experience to bring a different slant on your topic. The Internet is so huge, it’s a good bet there are many other websites about your topic. The difference is they don’t have you. Capitalize on that to make fresh and unique content.
- Use a spell-checker. Many spelling errors and a sloppy design are two sure-fire ways for your website to scream ‘amateur’!
2. Utilize long-tail keywords.
I heard an explanation of long-tail keywords from a man who lamented of ever making the cover of Sports Illustrated’s swimsuit issue. He thought if he could get them to change the rules, he’d have a better chance.
So he decided to ask if they’d open it up to men. Then he realized there are a lot of men he’d have to compete against. So maybe if it was only open to men who lived in Texas. Hmmm, still lots of competition. How about men who lived in Seguin, TX? That’s better, but still a little too much competition. He finally decided on asking if they’d open the competition to men, who lived in Seguin, TX, who were bald, and who owned a canary. He figured that way he’d have a pretty good shot at winning it!
It’s pretty much the same with long-tail keywords. Find a small, sub-niche of a category and you’ll have less search volume, but less competition. Just be careful that you don’t focus so tightly there isn’t anyone interested in your topic at all.
More people are now searching on long-tail keywords, such as ‘home remedies for dandruff’, rather than just ‘dandruff.’ That means you don’t have to guess what that visitor wants or run an A/B test, he’s already told you. If you have a page that meets his criteria you have a pretty good shot at converting him into a customer.
3. Make your site easy to navigate both for visitors and search engines.
Think about how visitors will use your website. Can you group your individual pages into a few different groups? If so, make a general page for each group and then pages within that group or even sub-groups with pages within that group. Just don’t go too deep because the URLs will become unwieldy. Additionally many search engines won’t crawl very deep into your site because they figure your most important pages will be near the top of the hierarchy.
Along those same lines, group all of your images in a separate upper-level directory to simplify the path to them.
To further help visitors and search engines, create sitemaps for each. The sitemap for visitors can group your content by main categories, plus your additional pages like the About Us, Contact and Privacy Policy pages. For search engines, you should create a file named XML Sitemap. If you’re using WordPress there are plugins that will make this file for you.
4. Check your title and description meta tags.
Meta tags belong in the HEAD section of your web page. This is where the page’s setup starts, although this section doesn’t show directly to the visitor. You can see it by clicking on Ctrl-U (Command-U on a Mac). You can also use the tool bar in your browser.
The title meta tag – <meta name=”title” content=”Starbucks Homepage”> – is similar to the <h1> tag, but this is the text Google will generally show as a link to your page in the search engine results. (By the way, can you think of a different title rather than ‘Starbucks Homepage’ for better SEO? Hint – What is their famous product?)
The description meta tag gives the search engines a summary of what your page is about. This is usually the text Google will show just after your page’s link in the search engine results. However, depending on the visitor’s query, Google may choose a snippet off your page to show instead.
Be sure to use a unique title and description for each page on your website to help visitors find the information they need. Also avoid using too much information (such as filling it with keywords) or too little information (‘this is a web page’).
5. Use the author tag to get credit for your content.
(Updated for 2019: Although this seemed like a good idea, it never gained much traction and is no longer available)
In Google’s quest to deliver the best and most relevant content to searchers, they’re now connecting authors with their content. The idea being a good author will provide good content no matter where he or she is writing.
Adding this link to your articles can make a big difference in how your content appears in the search results. If you haven’t already, sign up for a Google account and fill out as much information as you can. Be sure to include a photo of yourself. And add the name and complete URL of your website (and anywhere else you contribute).
When you’re finished, grab a copy of the URL. It should look something like this – https://plus.google.com/111186258783174834786/. You specifically want that long string of numbers. That’s your unique identity to Google.
Now go to your website and create your author bio, including a link back to your Google profile. If your bio included a line like ‘Connect with me on Google ‘ and you wanted the words ‘connect with me’ to be the anchor text, use code like this –
<a rel=”author” href=”https://plus.google.com/111186258783174834786/”>connect with me</a>
– replacing the string of numbers with your unique number.
After it’s all connected, when your content appears in the search results there will be additional information presented. That information can include your photo, plus your name and number of people within your Google circles. Why do you want this additional information? Because according to SocialMediaExaminer.com, “people are more likely to click on links associated with author images and profiles than those without.”
6. Use the heading tags on your pages correctly.
Heading tags change the formatting of text and give visitors visual clues that these words are important. The tags are also important to search engines.
<h1> is an heading tag that means ‘Heading 1’ and tells the search engines that this is the title of the page. They will generally display this text in the clickable, first line of results. Make sure it’s descriptive and unique for each page. When you’re trying to come up with a good title, think of your favorite book titles. They give you an idea of the book’s content and sometimes use a play on words or something enticing to catch your interest.

Formatting A Subheading in WordPress
Sometimes when you use software to build your website, it will give each page a temporary title such as ‘New page 1’ or even ‘untitled.’ Be sure to change it to tell your visitors what your page is about. And don’t use the same title on more than one page; every page’s title should be unique.
Make your content easier to read, particularly for people who skim, by using sub-headings. The <H2> tag tells the browser to display the text a little bit different to catch the eye of your visitor. It also gives the search engines another clue about the contents of your page.
7. Use bold and italics to highlight certain words.
Have you ever read an article where a word or two was highlighted and you slowed down to emphasize that word in your head? Yep, just what the author wanted you to do. It’s human nature.
Will it help your page ranking? A little, maybe, but probably not much. However if it helps your visitors understand and like your content, their actions can affect your rankings. So do what you can to spice up your writing – just don’t go overboard.
Try highlighting a word or two to make the reader sit up and take notice. You can also use lists to break up lots of text. And keep your paragraphs short. Many short paragraphs are easier to digest than one, long, ongoing paragraph. Also don’t forget about using sub-headings at the beginning of each section to help visitors find just the content they want.
Things not to do:
- Bolding an entire paragraph.
- Emphasizing just your keywords.
8. Use ALT and caption tags for your images.
Have you ever gone to a website and where there’s supposed to be an image all you see is a red X? Don’t you wish you could see that image? Webmasters try to keep all links up to date, but stuff happens.
You can use the ALT tag to specify alternative text for the image if it can’t be displayed. It’s also helpful for people who are visually impaired and for search engines who can’t ‘see’ images.
Along that same vein, don’t put important text in an image. Because search engines can’t see it, they can’t index it, which means that content won’t help your page get found.
It doesn’t make visitors happy either. I love searching for new recipes to try and I’ve seen some websites post pictures of the entire process – this is good – however they print the ingredients and the directions on the images – not good. I like to save the recipe on my computer for later, rather than trying to remember where I found it or copy each picture and hope I didn’t miss any of them.
Using the caption tag in addition to the ALT tag gives you one more place to tell visitors and the search engines what your page is about. Use this tag to describe the image in a slightly different way and perhaps include a portion of your keyword phrase.
9. Use simple to understand names for your files and links.
Descriptive names will help visitors and search engines understand what your content is about. Names like page1.htm or pic.gif are of no help. Names that are too long or filled with keywords are not helpful either.
When people link to your content, they often use the URL as anchor text. Which do you think would get more clicks?
http://www.example.com/en/dir1/1054890/x2/000016a.htm
or
http://www.example.com/how-to-cook-a-pork-roast.htm
10. Link to other pages.
One of the greatest aspects of the Internet is linking to other pages and websites for more information. Make it clear what the page you’re linking to is about. Anchor text – the highlighted part that you would click on – should be a 2-3 word summary about that page. That’s much more useful than anchor text that says ‘click here.’ Visitors like links to more information and the search engines like it, but don’t overdo it. A 200-word page with 50 links is a bit much.
Be sure to link to other pages on your website from within the various pages. If you have a comprehensive topic and have written several pages of step-by-step directions, break it into several pages. At the end of the step 1 page add a link to step 2. At the end of the step 2 page add a link to step 3 – and also back to step 1 in case a visitor landed on page 2 and wants to start at the beginning. If you mention a concept on one page and have another, more detailed page about that concept link to it. Your visitors will thank you.
11. Avoid penalties for duplicate content.
If you have duplicate content, the quickest way to deal with it is to remove it.
In the past, people were posting duplicate content to article collections and to networks of sites with links back to the original to get better rankings in the search engines. When Google rolled out the Panda algorithm those sites tanked.
Sites with duplicate content will still be penalized. But sometimes you need that duplicate content – such as sales pages for products with various options or printer-friendly versions of pages made in PDF.
If you have duplicate content on your website, you need to tell the search engines that the content is a known duplicate, but is needed to enhance the visitor’s use of the website and that the original source can be found at a specific location.
For example, a website that has several ways to access the same product for sale – eg 14″ frypan, green frypan, brandname frypan – can use a canonical link to the preferred URL. I In the <HEAD> section of each of these pages you would add something like <link rel=”canonical” href=”http://example.com/frypans/brandname-frypan/”> if ‘brandname-frypan’ is the preferred page.
12. Choose which pages and directories search engines are allowed to index.
Search engines use software code to crawl and index content on the web. These bits of code are called ‘robots’ or ‘bots’ or ‘spiders.’ To control what these spiders see you can use a file titled ‘robots.txt.’ It must be placed in your root directory, for example ‘http://example.com/robots.txt.’ If you place it in a subdirectory – for example, ‘http://example.com/folder/robots.txt’ – the spiders won’t find it.
Within the robots.txt file you can tell the search engines if there are pages or even entire directories you don’t want indexed.
You generally want these spiders to find your content, but sometimes you want to stop a page from being indexed. Why, you ask? Each page on your website shares a little bit of the link juice passing to it, and link juice is a good thing because it helps your pages rank higher. But you have pages such as ‘Contact Us’ and ‘Privacy Policy’ for your visitors although they don’t add anything to your rankings. You’d want to stop those pages from being indexed and leaking some of that link juice. To do that, use the robots meta tag – eg <meta name=”robots” content=”noindex”> and place that in the <HEAD> section of just those pages. You definitely don’t want it on any of your important pages because the meta tag will prevent the page from being listed in Google’s web index!
The robots file is another way to prevent pages from being listed, but only if no other websites link to it. If you use the robots meta tag to stop a page from being crawled, don’t include that page in the robots.txt file. If the spiders are not allowed to crawl a page because of the robots.txt file they can’t see the meta tag directives and may index it anyway if another website links to it. The robots meta tag will completely block a page from being indexed.
Don’t rely on the robots file or meta tags to protect sensitive content. Instead encrypt it or place it within a password-protected subdirectory.
If you need help developing a robots.txt file for your website, Google offers a robots.txt generator in their Webmaster Tools.
13. Use a text browser to examine your site.
You’ve done all the work, now it’s time to see how the spiders see your website. If you’re using special features such as frames, JavaScript or Flash in your website, the spiders may have trouble crawling it.
Go to https://merabheja.com/12-text-only-browsers-for-browsing-in-slow-internet-connections/ to learn more about text-based browsers with links to each of the browsers they reviewed. Download one and give it a try. It’s a very different experience, but you’ll see whether the content you’ve worked so hard to create can be indexed by the search engines.
There you have it. Thirteen magical tips to make your website shine. Now I think it’s time to howl at that moon!
Last fall Google rolled out another algorithm update called Hummingbird. And every time they make a change, website owners scramble to ‘fix’ their websites.
Keywords are dead! My website will disappear! The sky is falling!
Whoa now! Stop and think a minute. You’ve been providing quality content on your website, haven’t you? If so, relax. Hummingbird is a good thing.
When Google changes their algorithm it’s to improve the search results.
Previous changes to the algorithms helped weed out results that were nothing more than keyword-stuffed crap. Hummingbird takes it another step further. It tries to determine the searcher’s intent from the context using conversational search.
According to Search Engine Land, “…Hummingbird is paying more attention to each word in a query, ensuring that the whole query — the whole sentence or conversation or meaning — is taken into account, rather than particular words. The goal is that pages matching the meaning do better, rather than pages matching just a few words.”
For example, say you need to fix your leaky faucet. In the old days, you’d probably use search shorthand and type ‘fix leaky faucet’ which would get you lots of links to plumbing companies’ websites.
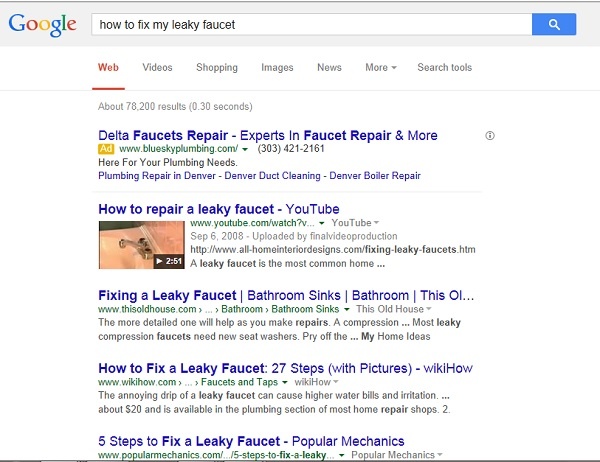
If you typed out the entire question ‘how to fix my leaky faucet’ you would probably still get some links to plumbing websites, but you would also get some ‘how to’ articles. Have you ever noticed some search terms are highlighted in the results? Those are the terms the search engine actually used – ‘fix’ and ‘faucet’.
With the Hummingbird algorithm, you might see a couple of plumbing company ads, but the organic results will be ‘how to’ articles. You will also see synonyms. Did you notice ‘How to repair’ instead of ‘How to fix’?
Google’s search engine continues to evolve.
People understand context. For example, you might start a conversation with a friend:
“Hey, I talked to Mary today.”
“Really? What did she say?
We know that ‘she’ refers to Mary, but to the old search engines those were two separate and different sentences. It couldn’t make the connection.
As Google’s Hummingbird develops it will better understand words and their relationships. It’s even starting to connect two queries which means it will know who ‘she’ is.
Do we need to change our SEO?
If you have original, high quality content, no.
However writing for users, rather than search engines, is more important than ever.
Here are some things to keep in mind:
- Use your key words, but also use synonyms. Remember both ‘repair’ and ‘fix’?
- In addition to quality, make your content specific. Instead of writing about ‘tomatoes’, write about ‘growing scrumptious tomatoes on an apartment balcony.’
- It’s still important that your titles be clear and straightforward. Keep in mind the needs and intentions of your readers.
- Also keep in mind users are generally looking for in-depth content that satisfies a need, rather than the ‘me too’ content.
Feel better now? It’s not such a scary thing. You can focus on your business and not worry about becoming an authority on SEO; just write quality content that your audience will love and Google will love you too. Promise.
You might also like:
- Learning more about how search works
We all use the Internet to find answers to our questions and the first thing we do is open our favorite search engine, type in a few keywords and click ‘search’.
If you’ve ever wondered what goes on behind the scenes, here’s a video from Google that will help explain what happens and how it decides which pages might interest you most.
As a small business owner, you should listen carefully to the questions Google asks about each page it finds because that will help you optimize your website for search engines so your site can rank higher and bring you more visitors.




